Molecular Bioelectrostatics & Drug Delivery Laboratory
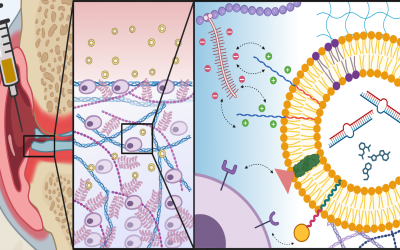
Located at Northeastern University’s Interdisciplinary Science and Engineering Complex (ISEC), the Bajpayee Lab works at the intersection of biomaterials design, nanomedicine and translational research. We utilize the body’s internal electric fields to design electrically charged biomaterials using proteins, peptides and cellular materials like exosomes, for targeting difficult to reach tissues for applications in drug delivery and diagnostic imaging.
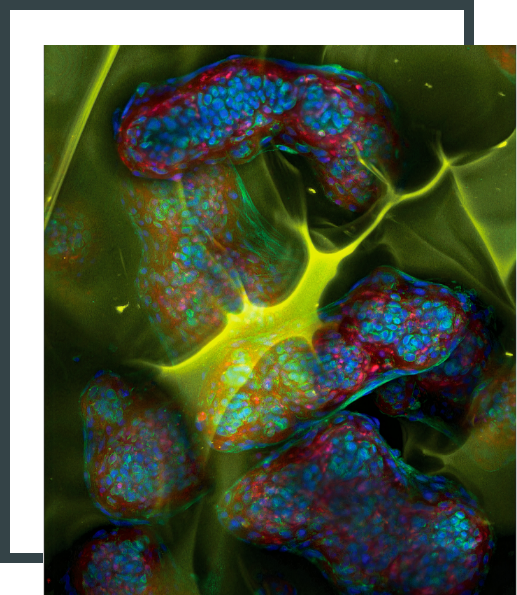
Negatively charged tissues such as cartilage, meniscus, intervertebral disc, eye, and mucosal membrane, that also tend to be dense and avascular, are ubiquitous in the human body but remain outstanding challenges for targeted drug delivery. Their degeneration is associated with several common diseases that remain untreatable due to a lack of delivery systems that can enable drugs to penetrate the negatively charged matrix and reach their cellular targets. The high negative fixed charge density, however, can be converted from being a challenge to an opportunity by engineering therapeutics at the molecular level to add optimally positively charged domains such that electrostatic interactions can enhance their transport, uptake and retention rather than hindering them. Our lab engineers targeted bioelectrical therapeutics for treatment of diseases affecting such intrinsically charged tissues. We strive to combine basic science with translational research to develop biomedical technologies for unmet clinical needs.
Follow us on Twitter @bajpayeelab | @AmbikaBajpayee

We are supported by

Our Lab News
Congrats to Andrew Selvadoss and Coauthors on the recently published review on exosomes for OA therapy in Nanoscale
We highlight the promise exosomes have as a next-generation therapy for OA and recent advances in engineering exosomes to enhance their targeted therapeutic potential. The paper is published in Nanoscale and can be accessed [HERE]!
Our newly minted PhD: Dr. Tanvi Vinod Pathrikar
Please congratulate Tanvi on her successful thesis defense on "Surface-engineered exosomes for targeted drug and gene delivery to cartilage" on Wed 9/25. We are wishing you best of luck on your future endeavor. We will miss you here in ISEC 262!
The 2024 nanoDDS in Orlando, FL: poster, talk, and award!
We had a great time sharing our research at the The 22nd International Nanomedicine and Drug Delivery Symposium (nanoDDS) in Orlando, Florida, September 13-15, 2024! Helna presented a poster on IL-1Ra mRNA delivery into cartilage using cationic-motif-modified exosome...